Growing global complexity in supply chain management has forced organizations to look towards technology as their silver bullet; serving as the missing link between people (supply chain actors) and the ability to collaborate at scale.
Blockchain technology is one of the most hyped amongst the currently developing technologies, hypothesized to make one of the greatest impacts in supply chain management — especially procurement and logistics — in the coming years. If SCM tech were a summer reading list, Blockchain would be the Twilight trilogy.
Simply put… Blockchain is on the brink of a majorly blowing up, and everyone wants to see what the hype is all about.
It was reported in mid-June by Zion Market Research that global “blockchain technology in supply chain management market was valued at around USD 40.99 million in 2017 and is expected to reach approximately USD 666.61 million by 2024, growing at a CAGR of 49.16% between 2017 and 2024” (globalnewswire.com 2018).
Hypotheses are coming to fruition, and technology vendors everywhere are looking to eat up their slice of that blockchain pie, as supply chain professionals begin to accept the value of blockchains’ applications within their organizations.
The decentralized/distributed ledger infrastructure excites transparency and traceability buffs, creating an even playing field for trusted data, accountability and streamlined governance. For this reason, blockchain technology has been viewed as the perfect match for business application within procurement and logistics.
Blockchain technology won’t just enhance the way procurement and logistics professionals work today; it poses the ability to reshape the functions entirely.
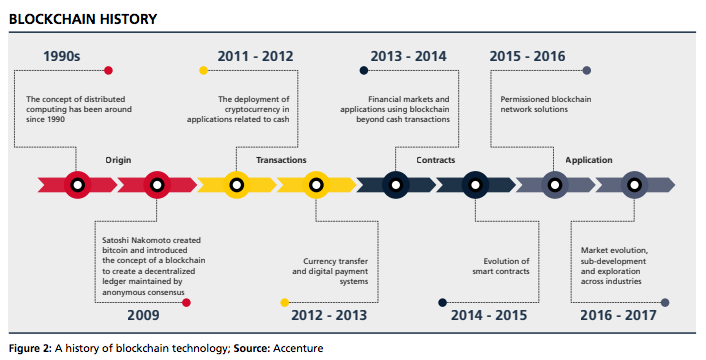
Below is a brief timeline of Blockchain’s history, and how it’s distributed computing infrastructure became widely famous for business application in the recent years.
Blockchain in Logistics
“Achieving excellence in logistics involves working collaboratively with others to optimize the flow of physical goods as well as the complex flow of information and financial transactions” (Gockel et al. 2018 p. 12).
Understanding the complexity of logistics, and keeping in mind the non-localized nature of today’s global supply chain, sets the scene for how difficult achieving logistics excellence can be in today’s new risk reality. This poses the question to logistics professionals on a daily basis: how does one continue to unlock value in logistics?
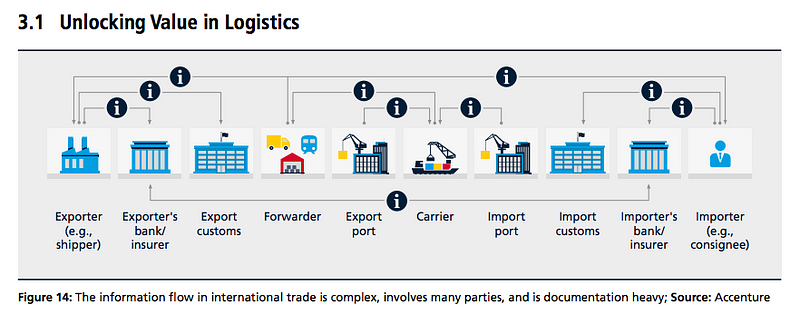
The image above illustrates that a typical logistics operation involves a lot of documentation, and even more information sharing. Logistics experts are reliant upon regulations, customs, papertrails, data entry and hands-on governance. All of these H2H (human-to-human) actions eliminate the agility needed to achieve logistics excellence, causing friction in delivery times, and ultimately disrupting global trade.
Blockchain poses the technological capabilities to achieve true logistics efficiency by streamlining, and even automating, processes in the logistics value chain that are heavily reliant upon H2H performance.
Below are some of the top applications for blockchain technology within logistics. These applications both support, but also disrupt current logistics roles.
This isn’t a question of if these applications will be realized; this is a question of when.
1. Leaner Trade, Better Wins
Because the amount of shipping and trade that occurs in the global supply chain has such close ties to the global GDP, the application of Blockchain within logistics can have a direct impact on the optimization of costs.
A great example of this is Maersk and IBMs venture that was launched in order to create a leaner stakeholder pool by digitizing end-to-end shipment tracking. This venture has the potential to eliminate massive costs previously tied to trade documentation and administrative processing for across-ocean shipments.
“Blockchain technology ensures secure data exchange and a tamper-proof repository for this documentation. The two companies expect this solution to track tens of millions of shipping containers annually. It has the potential to significantly reduce delays and fraud, which could lead to billions of dollars in savings in the logistics industry” (logistics.dhl 2018).
2. All Hands on Product
As published by TechCrunch, “A simple application of the blockchain paradigm to the supply chain would be to register the transfer of goods on the ledger as transactions that would identify the parties involved, as well as the price, date, location, quality and state of the product and any other information that would be relevant to managing the supply chain” (Dickson 2016).
Keeping a public ledger of all parties involved in a production process would add invaluable safeguards to the end-to-end logistics of a shipment. Because the ledger would be decentralized, no one party could manipulate the data sets. This means it would be simple to locate any disruptions, inefficiencies, fallacies or problem-origins.
3. Connecting IoT to the Blockchain
QR verification codes, and other sources of product verification, have been reshaping the limitations of logistics transparency for years. This same technology could be paired with blockchain technology, taking the reliability of data sets one step closer to certainty.

Tagging individual products, and creating individualized identifications within a blockchain ledger would secure data sets — regarding ownership — throughout the logistics lifecycle.
The connection between Blockchain networks and physical products will also improve the efficiency and reliability of 3PL and Warehouse Management. “The distributed database which is one of the main pillar of Blockchain concept, can used to get the inventory status across companies and even across the supply chain. The company can bring the important information of the warehouse to distributed database of Blockchain which can help companies to have a real time inventory status” (Verma 2017).
Blockchain in Procurement
Procurement and sourcing may very well be two of the greatest potential areas for impact when talking about blockchain application within supply chain management.
Transparency, Reliability and Trust are three words that are not always easy to come by in hands-on procurement. And, this is not at the fault of procurement professionals, but rather their current lack of technological application. Procurement excellence is highly reliant upon the compliance of first-tier, second-tier and even third-tier suppliers; the more parties involved in the process, the more complex collaboration becomes.
As stated previously, technology is the link between people and collaboration at scale. Procurement is most valuable when people (suppliers and buyers) are collaborating together and innovatively. To collaborate in the most innovative fashion, one should look to apply the most innovative technology.
The Kodiak Hub team, and I, strongly believe that Blockchain could offer that innovative edge that most procurement teams are looking for in both operational and strategic performance. But, we must remain realistic: Technology is a means to better performance in a value chain, but without the human knowledge or ability to utilize certain technologies, technology becomes a hindrance.
Looking at statistics from Deloitte’s 2018 CPO Survey below, one can see that the acceptance/application of blockchain technology in procurement isn’t quite as prevalent as I’ve just hypothesized it will — one day — become.
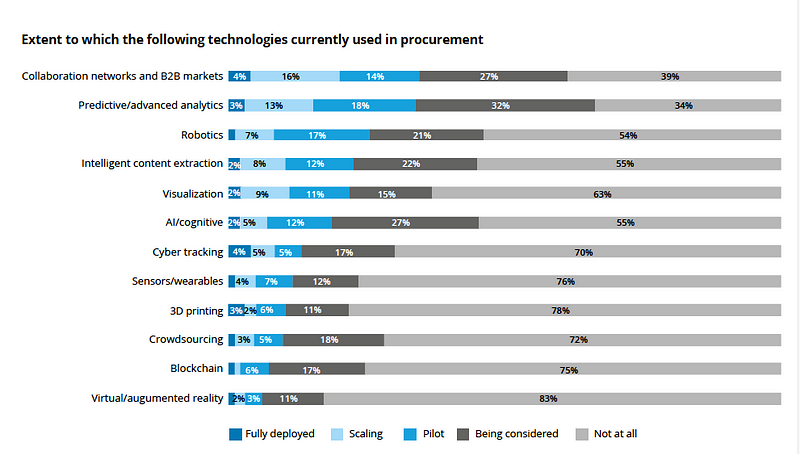
Let’s make a promise… We will continue to educate ourselves and keep one eye towards the future, as our other foot remains comfortably set in the sand. Because, while technology needs to meet the market where it is, it should also show the market where it’s heading next.
1. Tendering
On the more operational side of procurement-based activities, blockchain technology could be applied to enhance tendering for the best suppliers; leading to reduced costs and better quality/performance.
In fact, there is a Finnish startup that is already beginning the development of such a blockchain solution. “Kuovola Innovation is working on a blockchain solution that enables smart tendering across the supply chain. Pallets equipped with RFID tags publish their need to get from point A to point B on the ledger. Carrier mining applications will then place bids to win the move. The RFID will then award the job to the bidder with the most suitable conditions and the transaction will be registered on the blockchain. The shipment will be progressively tracked as the tag moves down the supply chain” (Dickson 2016).
2. Anonymous, Yet Transparent
Traders, agents and producers are aware of the necessity of supply chain transparency, but that doesn’t always mean they want to share sensitive information about their suppliers.
Blockchain technology offers the ability to balance transparency with anonymity (Kildune 2018).
“Many larger producers do not want to reveal provenance of their goods for fear of losing a competitive advantage. Blockchain allows information to be transferred in a trustworthy and anonymous way, essentially providing a trust network that allows information to cascade down the chain from raw material onwards, without revealing who people are” (Innovation Enterprise 2018).
3. Auditing & Governance
The permanency of data sets/efficiency of data entry onto blockchain networks offers opportunities for easy governance. This will help procurement teams to eradicate their supplier networks of defective supplier relationships.
“[Blockchain] will facilitate greater fraud control, and it will also offer transparency into issues of legality such as money laundering and the use of child labour” (idgconnect.com 2017). While blockchain safeguards fraud control in your suppliers’ organizations, it can also ensure authenticity of your physical production and eliminate counterfeiting.
When your procurement team is able to manage risk, secure sustainable development, safeguard brand value and enhance performance, it’s a pretty good day at the office.
4. Smart Contracting
Purchase-to-pay will never be the same again once technological vendors unlock the key to implementing blockchain networks at scale.
“Using smart contracts, where the terms are payable upon receipt, a proof of delivery from a logistics carrier will immediately trigger automatic digital invoicing and payments through the banking system, with no analog gap between customer and supplier. The result has the potential to radically reduce working capital requirements and dramatically simplify finance operations, with a direct impact to the bottom line” (Brody 2017).
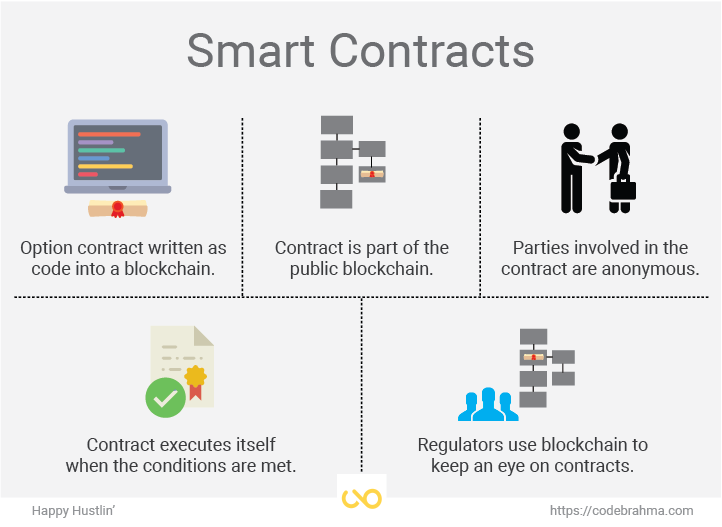
This is a hypothesis of application within a P2P solution, but a feasible one nonetheless. Smart contracting creates an ecosystem of financial reliability for procurement professionals and their supplier base.
5. Supplier Relationship Management
Blockchain technology builds transparency, but also accountability.
Ensuring that suppliers are accountable for their actions builds a platform for compliance and trustworthy relationships. Due diligence and risk management are inherent elements of a decentralized ledger for data entry. Put a bit simpler… trust recognizes trust.
Distributed data sets, over time, will allow procurement professionals and their suppliers to share a special collaboration, built upon a history of reliable performance data.
Hopefully, procurement teams can see the bigger picture, and will be open with distributing blockchain networks beyond their own organizations, and develop/join cross-organizational blockchain information networks. This could reduce competitive edge, allowing other competitor organizations to know what suppliers you’re working with, but it could also prove fruitful — eliminating/ousting untrustworthy suppliers within an entire industry sector.
As Kodiak Hub’s CTO, Ashley Stephenson, was once quoted, “in order to enact global change and impact, we must distribute the revolution.”
Learn more about how Supplier Relationship Management can help you.
Until next week.